Localizable.strings
Translation File Format
Localizable.strings is a file format used to store key-value pairs of translations in macOS and iOS applications. It's the traditional localization format for Apple platforms that has been widely used in Swift and Objective-C projects.
Localizable.strings file format
Localizable.strings is a simple text-based file format used to store key-value pairs of translations in macOS and iOS applications. Each line in a Localizable.strings file represents a single translation, with the key and value separated by an equals sign and enclosed in double quotes. The key is typically a descriptive string that identifies the translation, while the value is the translated text that will be displayed to users. Comments can be added to the file using /* and */ for block comments or // for single-line comments.
/* Login screen translations */
"login.title" = "Sign In";
"login.email" = "Email Address";
"login.password" = "Password";
"login.button" = "Log In";
/* Home screen translations */
"home.welcome" = "Welcome, %@!";
"home.notifications" = "You have %d notifications";
/* Error messages */
"error.network" = "Network connection failed";
"error.invalid_credentials" = "Invalid email or password";In most cases, one file contains translations for a single language. Each language has its own .strings file organized in language-specific directories (lproj folders). For example, you can have English translations in en.lproj/Localizable.strings and Spanish translations in es.lproj/Localizable.strings.
/* Login screen translations */
"login.title" = "Iniciar Sesión";
"login.email" = "Dirección de Correo";
"login.password" = "Contraseña";
"login.button" = "Iniciar Sesión";
/* Home screen translations */
"home.welcome" = "¡Bienvenido, %@!";
"home.notifications" = "Tienes %d notificaciones";
/* Error messages */
"error.network" = "Falló la conexión de red";
"error.invalid_credentials" = "Email o contraseña inválidos";File structure and organization
Localizable.strings files are organized in language-specific directories called lproj folders. Each language has its own directory that contains the translation files for that specific language. This structure allows Xcode and the iOS/macOS runtime to automatically load the appropriate translations based on the user's language preferences.
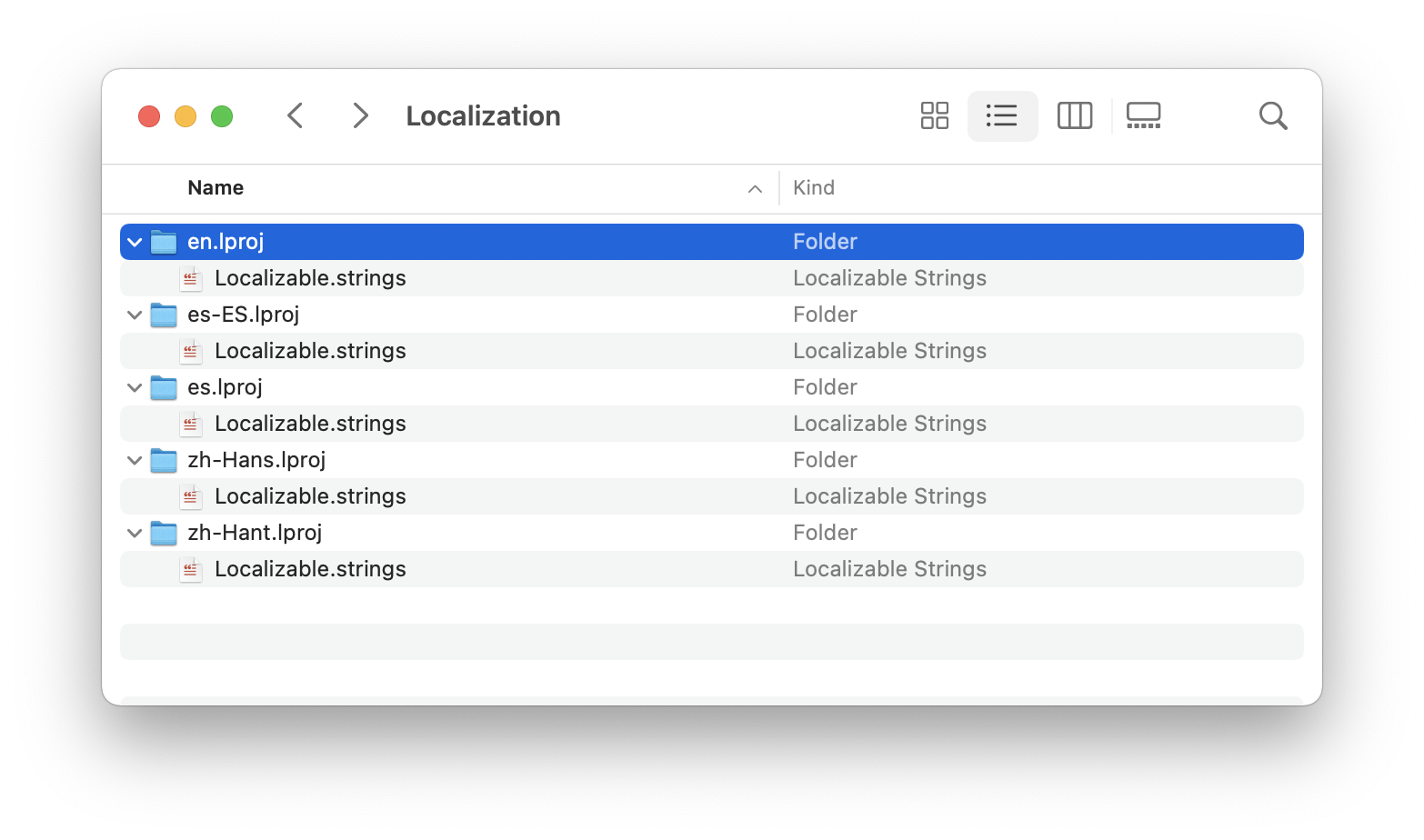
The typical file structure for a localized iOS or macOS application looks like this:
- en.lproj/Localizable.strings - English translations
- es.lproj/Localizable.strings - Spanish translations
- fr.lproj/Localizable.strings - French translations
- de.lproj/Localizable.strings - German translations
String interpolation and placeholders
Localizable.strings supports string interpolation using format specifiers similar to printf. You can use placeholders like %@ for strings, %d for integers, %f for floating-point numbers, and positional arguments like %1$@ and %2$d for more complex formatting scenarios.
/* Simple string interpolation */
"welcome.message" = "Hello, %@!";
"item.count" = "You have %d items in your cart";
"price.display" = "Price: $%.2f";
/* Positional arguments */
"order.summary" = "%1$@ ordered %2$d items for $%3$.2f";
"date.format" = "Today is %1$@ %2$d, %3$d";Using Localizable.strings in Swift
Swift provides built-in support for loading translations from Localizable.strings files through the NSLocalizedString function.This function automatically loads the appropriate translation based on the user's language settings and provides fallback mechanisms for missing translations.
How to use Localizable.strings in iOS/macOS?
Setting up localization with Localizable.strings in iOS and macOS applications involves creating the translation files, configuring your Xcode project, and using the appropriate APIs to load translations in your code.
"app.title" = "My Application";
"welcome.message" = "Welcome to our app!";
"button.continue" = "Continue";
"error.generic" = "Something went wrong";Create Localizable.strings files
1Project Settings → Info → Localizations
✓ English (Development Language)
✓ Spanish
✓ French
✓ GermanConfigure project localization
2import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
@IBOutlet weak var titleLabel: UILabel!
@IBOutlet weak var welcomeLabel: UILabel!
@IBOutlet weak var continueButton: UIButton!
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
titleLabel.text = NSLocalizedString("app.title", comment: "Application title")
welcomeLabel.text = NSLocalizedString("welcome.message", comment: "Welcome message")
continueButton.setTitle(NSLocalizedString("button.continue", comment: "Continue button"), for: .normal)
}
}Use NSLocalizedString in code
3NSLocalizedString function to load translations in your Swift code. This function takes the translation key and an optional comment for translators. The system automatically loads the appropriate translation based on the user's language preferences.// Using String.localizedStringWithFormat
let username = "John"
let itemCount = 5
let welcomeText = String.localizedStringWithFormat(
NSLocalizedString("welcome.user", comment: "Welcome message with username"),
username
)
let itemsText = String.localizedStringWithFormat(
NSLocalizedString("cart.items", comment: "Number of items in cart"),
itemCount
)
// Using string interpolation (iOS 13+)
let localizedFormat = NSLocalizedString("price.display", comment: "Price display")
let priceText = String(format: localizedFormat, 29.99)Handle string interpolation
4String.localizedStringWithFormat or string interpolation to insert dynamic values into your translations. This allows you to create more dynamic and personalized user interfaces while maintaining proper localization.Migration to Localizable.xcstrings
Apple introduced Localizable.xcstrings at WWDC 2022 as the modern replacement for Localizable.strings files.The new format provides better tooling support, improved collaboration features, and enhanced metadata for translations. While Localizable.strings files continue to work, Apple recommends migrating to the new format for new projects.
Key differences between .strings and .xcstrings
- Single file vs. multiple files: .xcstrings stores all languages in a single JSON-like file, while .strings requires separate files for each language
- Better tooling: Xcode provides enhanced editing and validation tools for .xcstrings files
- Metadata support: .xcstrings includes extraction state, translation status, and comments in the file format
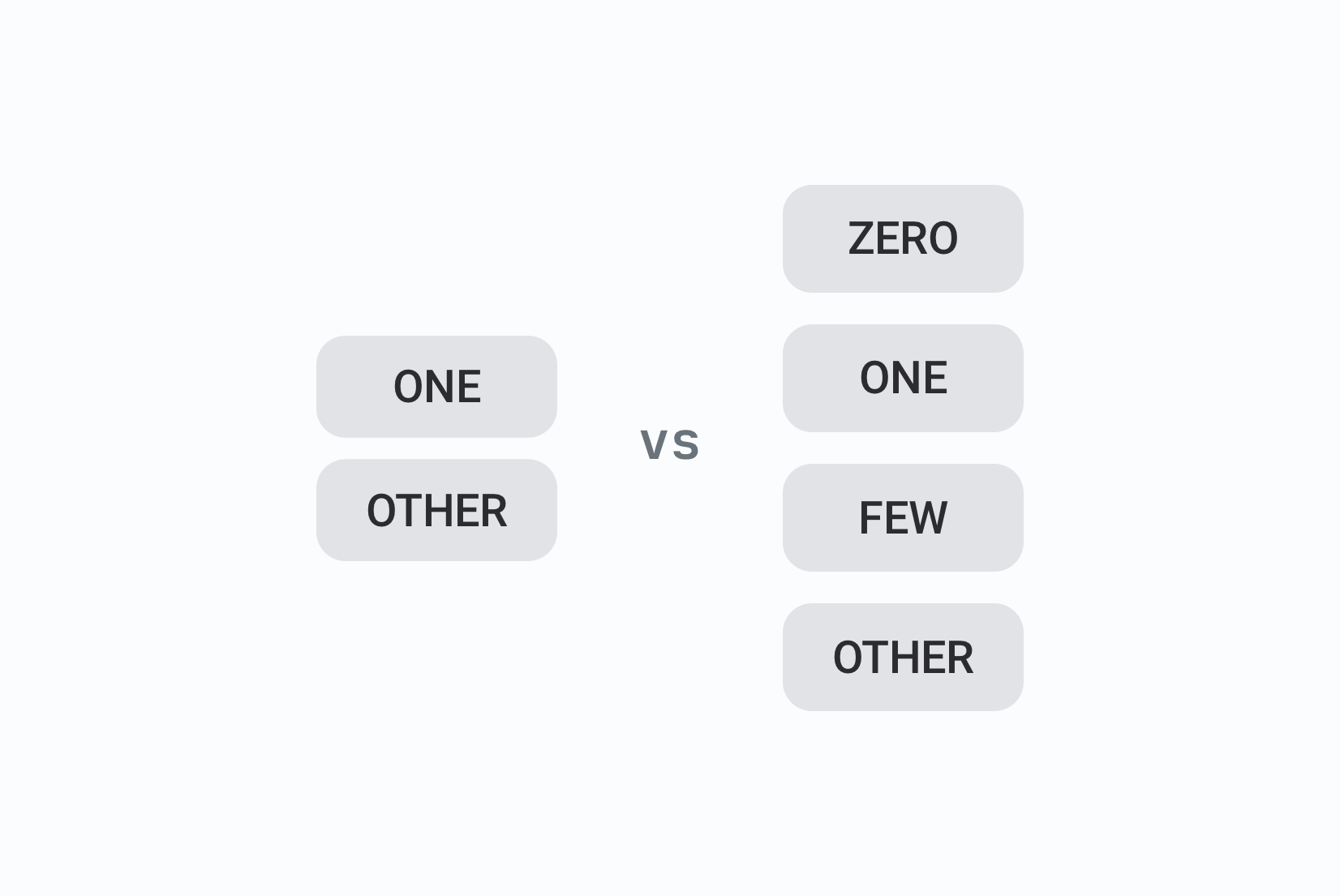
- Pluralization: Native support for plural forms without requiring separate .stringsdict files
- Device variants: Built-in support for device-specific translations
Learn more about Localizable.xcstrings file format and how to migrate your existing .strings files to the new format.
Where Localizable.strings is used?
Localizable.strings files are primarily used in Apple platform development for iOS, macOS, watchOS, and tvOS applications. They work with both Swift and Objective-C programming languages and are supported by various Apple development frameworks.
iOS
macOS
Swift
SwiftUI
Objective-C
Xcode
Best practices for Localizable.strings
To effectively manage translations in Localizable.strings files, follow these best practices:
- Use descriptive keys: Choose clear, hierarchical keys that describe the context and purpose of the translation
- Add meaningful comments: Provide context for translators using the comment parameter in NSLocalizedString
- Organize by feature: Group related translations together and use consistent naming conventions
- Handle missing translations: Always provide fallback text and test with unsupported languages
- Use genstrings tool: Leverage Xcode's genstrings command-line tool to extract translatable strings from your source code
- Keep translations in sync: Use tools like SimpleLocalize to manage translations across multiple languages and maintain consistency
How to keep Localizable.strings files in sync?
Managing translations across multiple Localizable.strings files can be challenging, especially when supporting many languages. Adding, updating, or removing translations requires changes to multiple files, which can lead to inconsistencies and missing translations. To streamline this process, you can use SimpleLocalize and its translation editor to manage all your translations in one place.
With SimpleLocalize, you can upload your Localizable.strings files, edit translations in a user-friendly interface, collaborate with translators, and download updated files for all languages. Features like auto-translation, bulk operations, and CLI integration help keep your translations synchronized and up-to-date across all platforms.
Meet SimpleLocalize
Your partner in managing translations and localization workflow.
Web-based translation editor helps iOS and macOS developers keep their Localizable.strings files in sync.

- Auto-translation
- Screenshots with OCR
- AI-powered adjustments
- Built-in Automations
- Markdown support
- Variables highlighting
- Bulk Actions
- Context-aware translations
- Acceptance statuses
- Quality checks
- Comments & mentions
- Real-time collaboration
Auto-translation
Translate your application into multiple languages with just a few clicks. Choose from OpenAI ChatGPT, Google Translate or DeepL translation providers to translate your texts. Adding support for new languages has never been easier.
Learn more about auto-translation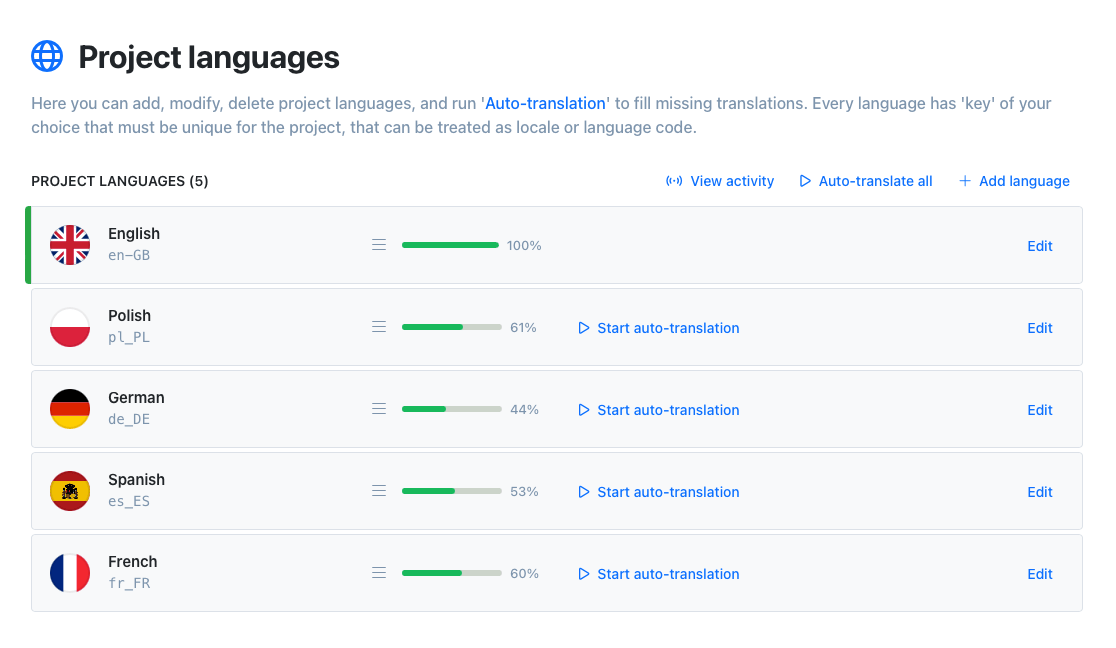
Command-line tool
With SimpleLocalize CLI you can manage your translations from the terminal. It's a powerful tool that helps you to automate the translation process in your project. You can easily synchronize translation files between you local project and SimpleLocalize Translation Editor, start auto-translation or publish changes to the production environment.
CLI documentation# upload source translations
$ simplelocalize upload
# auto-translate strings
$ simplelocalize auto-translate
# download translated files
$ simplelocalize downloadCommunity suggestions
Engage your community in the translation process with public suggestions. Let users propose improvements directly, helping you refine translations and build engagement. Enable public suggestions for your project, share the link, and start collecting input.
Learn how to collect translation suggestions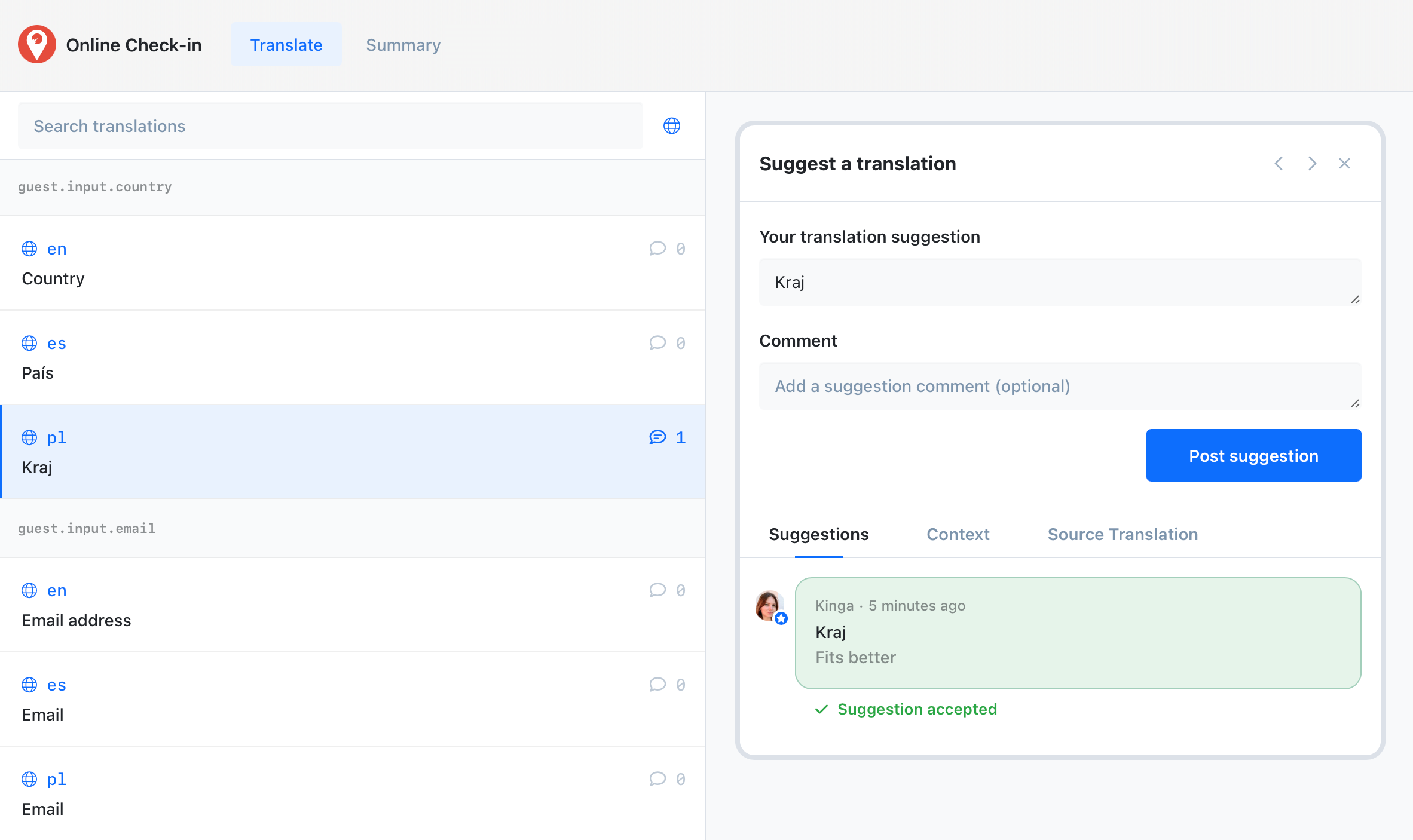
Get started with SimpleLocalize
- All-in-one localization platform
- Web-based translation editor for your team
- Auto-translation, QA-checks, AI and more
- See how easily you can start localizing your product.
- Powerful API, hosting, integrations and developer tools
- Unmatched customer support