What is localization QA? Definition, benefits & best practices

Ever seen a button on a website with text spilling out of it, or a date format so confusing you weren't sure if you'd booked for January or December? That's what happens when Localization QA gets skipped.
When you are growing your business internationally, translating your product is just the first step. What really makes or breaks the user experience is Localization QA (Quality Assurance), the process of making sure your product feels right for users in every market.
Skipping this step can lead to confusing, clunky, or even embarrassing results. But with the right approach and tools, like SimpleLocalize, you can make localization QA smooth, collaborative, and stress-free.
What is Localization QA?
Localization QA (often shortened to LQA) is the process of reviewing localized content inside the product itself to check:
- Does the text fit properly in the design?
- Is the translation accurate and natural in context?
- Are dates, currencies, and units adapted to the local market?
- Does the interface still work correctly after localization?
It's not just about correct grammar, but delivering a product that feels like it was created locally from the ground up. Think of LQA as the final dress rehearsal before launching your product on the global stage.
Why is Localization QA important?
Let's look at some practical examples. Imagine you are translating a hotel booking website.
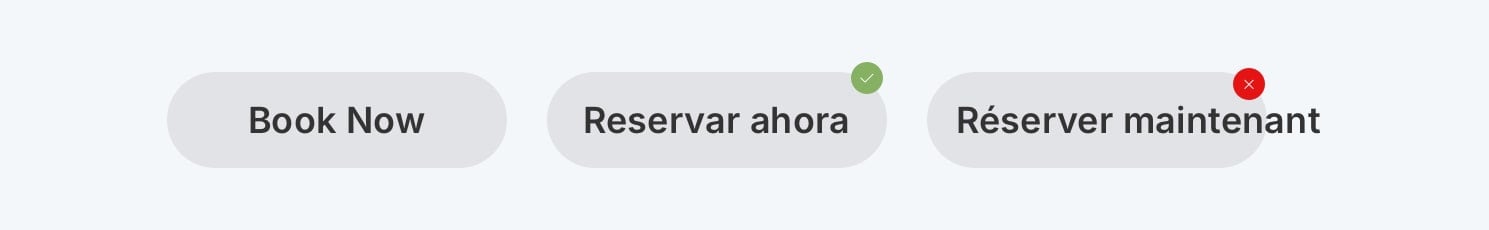
Example 1: The "Book Now" button in French becomes "Réserver Maintenant". If the button is too small, the text might overflow, making it hard to read or click.
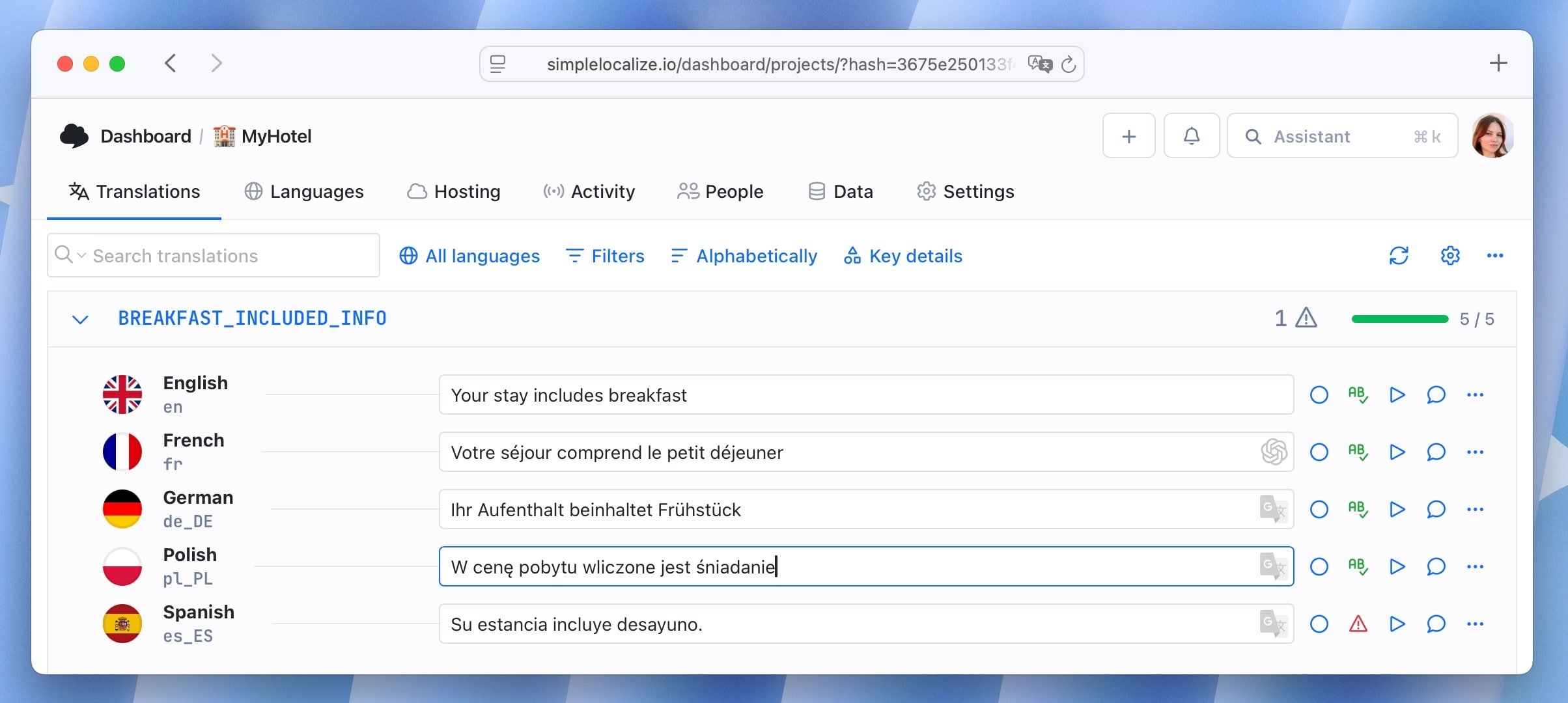
Example 2: "Your stay includes breakfast" is translated by Google Translate to "W cenę pobytu wliczone jest śniadanie" in Polish. While accurate, a more natural phrasing would be "Śniadanie wliczone w cenę pobytu".
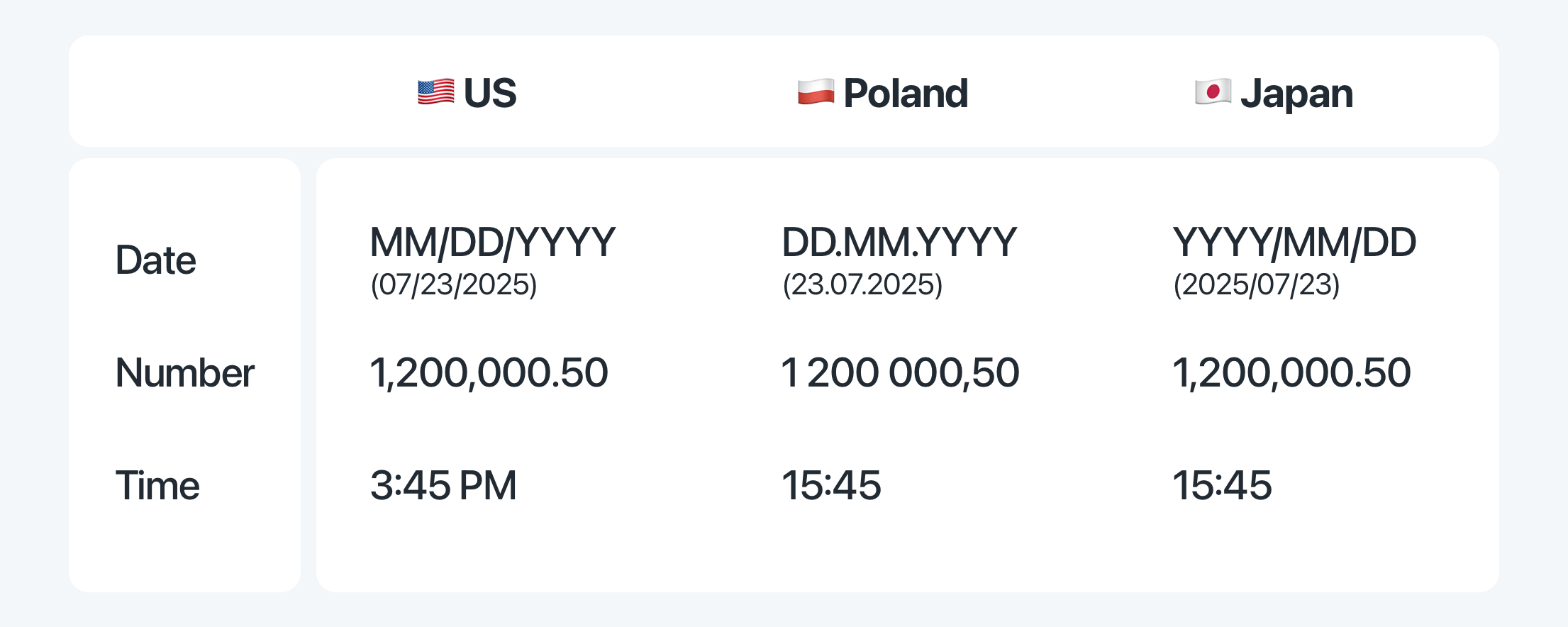
Example 3: The date format "MM/DD/YYYY" is used in the US, but in Germany, it should be "DD.MM.YYYY". If this isn't changed, users might get confused about their booking dates.
These small details can lead to big problems if not caught during Localization QA:
- Text length issues. If the translated text is too long, it might break the layout, making buttons hard to click or text unreadable.
- Overly literal translations. If the translation is too literal, it might sound awkward or confusing to native speakers.
- Date and number formats. If formats aren't adapted, users might misinterpret booking dates, prices, or measurements, leading to frustration.
- Broken functionality. If interface elements don't function properly after localization, users may encounter bugs or errors.
- Cultural disconnects. If cultural references aren't adapted, users might feel the product is out of touch with their local context.
- Visual elements. If images or icons aren't appropriate for the local culture, users might feel alienated or confused.
- Device compatibility. If localized content isn't tested on different devices and screen sizes, users may have a poor experience on mobile or tablets.
How Localization QA is done
A typical LQA process involves:
- Linguistic review: Making sure the translation is natural, consistent, and follows tone guidelines.
- Functional testing: Checking if placeholders (
{name},%d, etc.) and plural rules work properly. - Visual/UI testing: Ensuring text isn't cut off or breaking layouts. For example, French tends to be ~20% longer than English, and German can be even longer.
- Cultural review: Making sure images, colors, and references are appropriate. (For example, a US “mm/dd/yyyy” date format would confuse users in Europe.)
How SimpleLocalize helps with Localization QA
Managing all of this across spreadsheets, translators, and developers can quickly get overwhelming. That's where SimpleLocalize comes in.
With SimpleLocalize, you can:
- Collaborate easily: Developers, translators, and QA testers work in one platform, reducing back-and-forth emails.
- See translations in context: Preview them in your app or website to avoid guesswork (use in-context editor, add screenshots and descriptions).
- Catch UI issues early: Ensure text length, placeholders, and RTL (right-to-left) languages like Arabic or Hebrew are handled correctly.
- Automate checks: Validate placeholders, plural rules, and formatting before they cause bugs.
- Track the review process: Leave comments and approve translations when ready.
- Centralize your localization: No more scattered spreadsheets; all your translations live in one place.
Learn more about live automated QA checks and using review status in SimpleLocalize.
Best practices for effective Localization QA
To get the most out of your Localization QA process, keep the below tips in mind.
People
- Involve native speakers: They can catch nuances, idioms, and cultural references that non-native speakers or machine translation might miss.
- Engage with local communities: Whenever possible, gather input from real users in your target markets—nothing beats authentic feedback. Use our public suggestions feature to collect ideas and corrections from your user base.
- Communicate and document clearly: Make sure translators, developers, and testers understand expectations. Document decisions and feedback to improve consistency over time.
Process
- Plan for localization early: Integrate localization into your design (Figma plugin) and development process (check GitHub integration) from the start; this avoids costly layout fixes later.
- Use a standardized QA checklist: Define what to check—text length, placeholders, date formats, tone, visuals, so nothing slips through the cracks.
- Prioritize and iterate: Focus QA on your key markets first, gather feedback from users, and use analytics to refine future releases.
Technology
- Test in context and on real devices: Always check how translations look and work within the actual product across different screen sizes, operating systems, and browsers.
- Leverage technology: Tools like SimpleLocalize help streamline collaboration, automate format checks, and centralize translations so your QA process is faster and more reliable.
- Automate where possible: Use automated tests to catch common issues like missing placeholders or formatting errors before they reach human reviewers.
Conclusion
Localization QA isn't just quality control, it's an investment in trust. When users feel at home in your product, they are far more likely to stay, recommend it, and come back.
By combining best practices with a translation management tool like SimpleLocalize, you can make QA faster, easier, and more reliable. The result? Happier users, smoother global launches, and a product that truly speaks your customers' language.
Ready to make localization QA a breeze? Try SimpleLocalize today and see how much easier managing translations can be.
FAQ
What is the difference between QA and Localization QA?
General QA (Quality Assurance) checks whether a product works correctly: functionality, performance, usability. Localization QA (LQA) focuses specifically on how well the product has been adapted to different languages and cultures, ensuring it feels natural for users in every market.
When should Localization QA be done?
LQA should be integrated throughout the localization process, not just at the very end. Early checks (in design and development) catch issues like text expansion or date formats before they become costly to fix. Final reviews should happen just before launch to ensure nothing slipped through.
Who is responsible for Localization QA?
It's usually a shared responsibility:
- Translators ensure linguistic accuracy and tone.
- QA testers check functionality and UI layout.
- Developers handle placeholders, formatting, and technical aspects.
- Product managers or localization managers coordinate the process.
What are the most common localization QA issues?
- Text that's cut off or too long for buttons/menus
- Literal translations that sound unnatural
- Wrong date, time, or number formats
- Missing or incorrect placeholders
- Cultural mismatches in images, icons, or colors
- Functionality bugs after localization
- Inconsistent terminology across the product
Can automation replace human Localization QA?
Automation and live QA checks can catch technical issues like placeholder errors, missing translations, or wrong date formats. But only native speakers can judge naturalness, cultural appropriateness, and overall user experience. The best approach is combining automation with human review.
How does Localization QA improve user experience?
LQA ensures users don't stumble over confusing text, broken layouts, or awkward translations. A product that feels local builds trust, reduces errors, and increases user satisfaction, which directly impacts retention and conversions.
Do small startups really need Localization QA?
Yes. Even for small teams, LQA prevents embarrassing mistakes and support issues. Starting with basic checks and leveraging tools like SimpleLocalize helps scale QA as you expand to more markets.