AI-Powered localization workflows for software translation

AI is transforming how software teams translate and localize their products, shifting from slow, manual processes to automated, context-aware workflows that run alongside your code deployments. With the right setup, you can go from “feature merged” to “available in five languages” in hours, not weeks.
This guide focuses on AI-powered localization workflows: how to integrate them into your development process, choose the right tools, and keep translations accurate without slowing down your releases.
Why AI is a game changer for localization
Traditional localization workflows are often slow and repetitive:
- Extract text from code.
- Send it to translators.
- Wait for files to come back.
- Merge, fix, and redeploy.
This cycle can take weeks, especially for large applications with multiple languages.
AI speeds this up by providing:
- Instant draft translations for any language.
- Scalable updates for new features across all supported locales.
- Lower costs by reducing human translator time on first-pass content.
- Integration into CI/CD so translations happen automatically with each build.
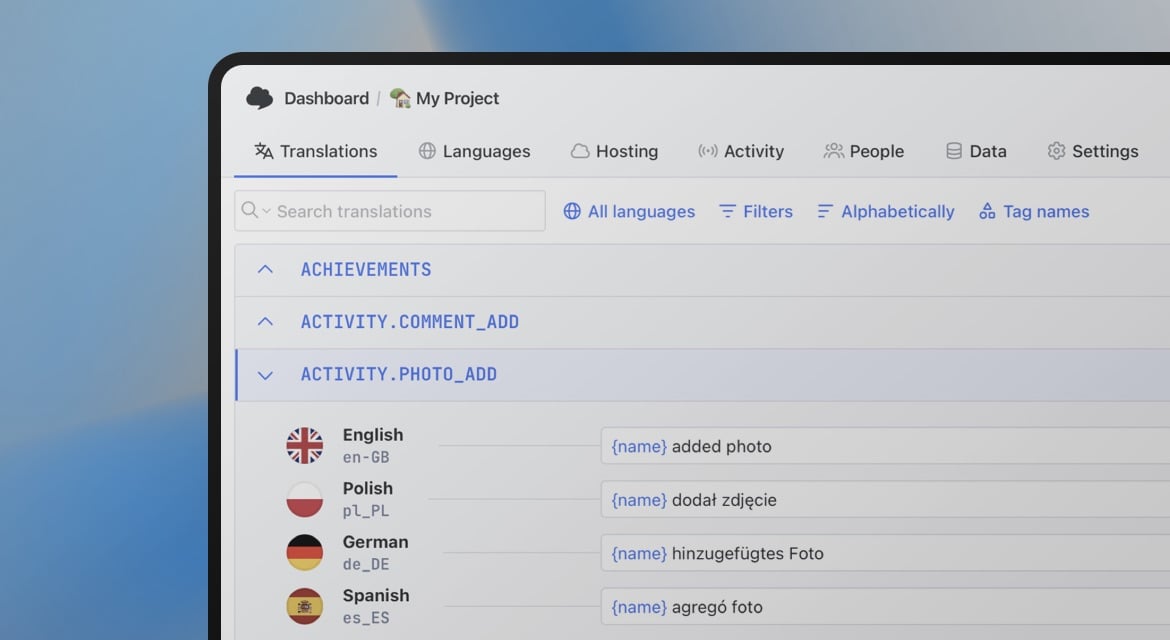
When combined with developer-friendly platforms like SimpleLocalize, AI translations can run as part of your pipeline, turning localization into just another automated build step.
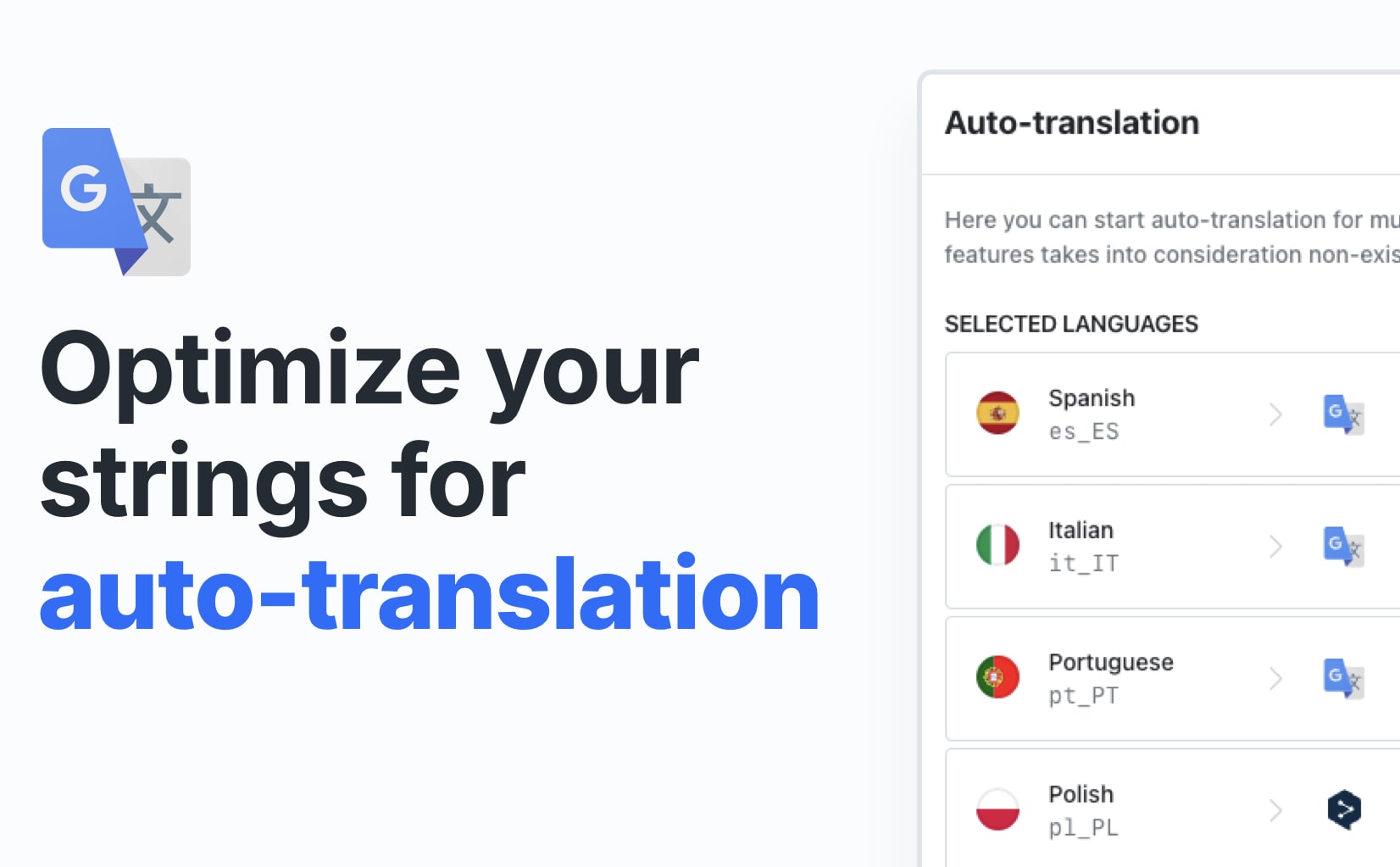
Choosing the right AI provider
Each AI translation provider has strengths. Your choice depends on tone, accuracy needs, language coverage, and cost.
| Provider | Best for | Standout features |
|---|---|---|
| OpenAI | Natural, human-like text | Flexible tone/style prompts |
| DeepL | European languages, high accuracy | Great with idioms and context |
| Google Translate | Wide language coverage, low cost | Instant translations at scale |
| Microsoft Translator | Enterprise, Azure integration | Easy ecosystem fit |
When selecting a provider, consider:
- Tone requirements (marketing vs. technical documentation)
- Language coverage (do you need rare languages?)
- Integration ease (API, SDKs, CLI tools)
- Cost (tokens vs. characters, free tiers)
For a deeper translation output comparison, see our AI & machine translation comparison.
Also, check out our complete list of machine and AI translation providers to see all available options.
Tools for smoother localization workflows
AI translation is just one piece of the puzzle. Here are some essential tools and features that make localization easier for developers:
- Pseudo-localization for layout and overflow testing (e.g., using In-context Editor).
- Grammar/style QA, e.g., LanguageTool.
- IDE integrations to manage strings without leaving your editor (e.g., SimpleLocalize VS Code extension or IntelliJ plugin)
- Continuous integration checks catch missing keys or placeholders before deployment.
- Translation memory to reuse existing content and cut costs.
These tools pair well with SimpleLocalize's CLI, API, and automations for a fully scripted translation pipeline.
Example workflows for AI-powered localization
Below are five common approaches to integrating AI into localization workflows. Pick the one that fits best your release process.
CLI + manual control
A hybrid approach: manual triggers with automation for speed.
Steps:
- Commit new feature code with new strings to your repository.
- Extract new strings (e.g., using FormatJS CLI).
- Push extracted strings to SimpleLocalize via CLI.
- Run AI translation via CLI.
- Download translations.
- Commit & deploy.

Sample pseudo code for CLI usage:
# Step 1: Extract strings
formatjs extract --out-file source.json
# Step 2: Upload to SimpleLocalize
simplelocalize upload --uploadPath source.json --languageKey en
# Step 3: Run AI translation
simplelocalize auto-translate
# Step 4: Download translations
simplelocalize download --downloadPath messages_{lang}.json
# Step 5: Commit translations
git add .
git commit -m "Add translations for new feature"
git push
Description:
This workflow gives you full control over when translations are updated and allows manual review before deployment. It's one of the most common approaches for teams that want to integrate AI translation without fully automating the process. You can also move part of the process to a CI/CD pipeline depending on your preferences.
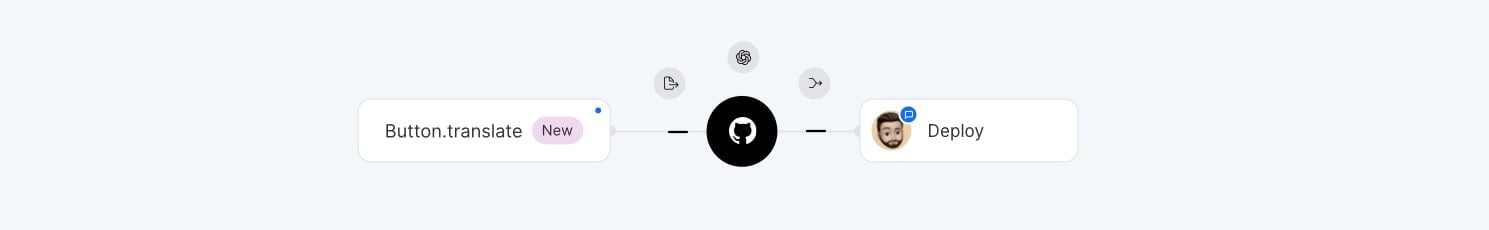
CLI + GitHub Actions
Automate the CLI steps with GitHub Actions to reduce manual work but keep review before deployment.
Steps:
- Push new code to your repository.
- GitHub Actions workflow runs automatically:
- Extracts new strings (e.g. with
formatjs extract), - Runs AI translation via SimpleLocalize CLI,
- Commits translations back to the repository.
- Extracts new strings (e.g. with
- Deploy the localized build.
Description:
This approach automates the translation process while still allowing you to review changes before they go live. Similar workflows can be set up with other CI/CD systems like GitLab or Bitbucket.
Fully automated publication
This is the most automated approach, ideal for teams aiming for “zero-touch” localization.
Preconfiguration steps:
- Set up automation in SimpleLocalize to run AI translation automatically on new strings.
- Configure automation to publish translations immediately after AI translation completes.
Localization workflow:
- Commit new feature code with new strings to your repository.
- Extract new strings and push them to SimpleLocalize (e.g., using FormatJS CLI).
- SimpleLocalize detects changes, triggers AI translation automation, and publishes translations automatically.

Description:
Your app receives updated translations instantly without manual intervention or the need to redeploy.
The downside is this may lead to unreviewed translations going live, so this workflow is best when speed is more important than perfect accuracy.
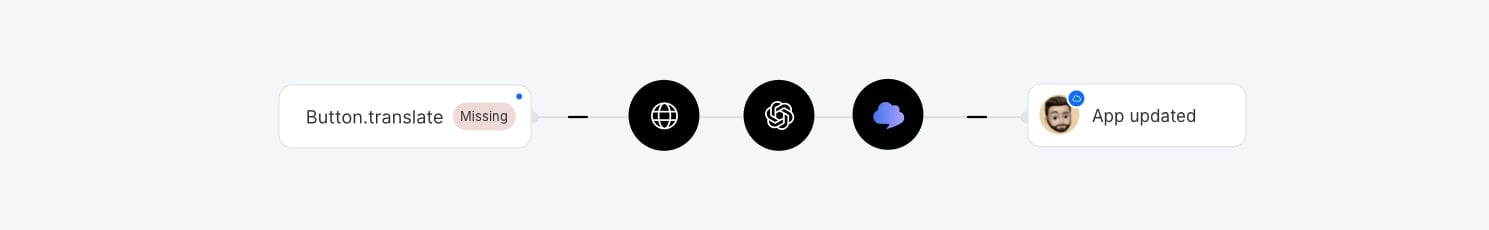
Continuous localization via i18next
A popular setup for JavaScript apps that combines AI with continuous translation of missing keys using the i18next library.
Steps:
- Configure the
missingKeyHandlerfunction to automatically create keys when missing translations are detected. - Set up SimpleLocalize automation to run AI translation on new keys and publish updates.
- Your app always has the latest translations without manual steps.
Description:
This approach works well for apps with frequent string changes, ensuring translations stay current automatically. Translators can review and improve AI-generated content in the SimpleLocalize editor after generation.
The downside is it may create many unused keys, requiring manual cleanup. Check out our guide on cleaning unused keys to help with that.
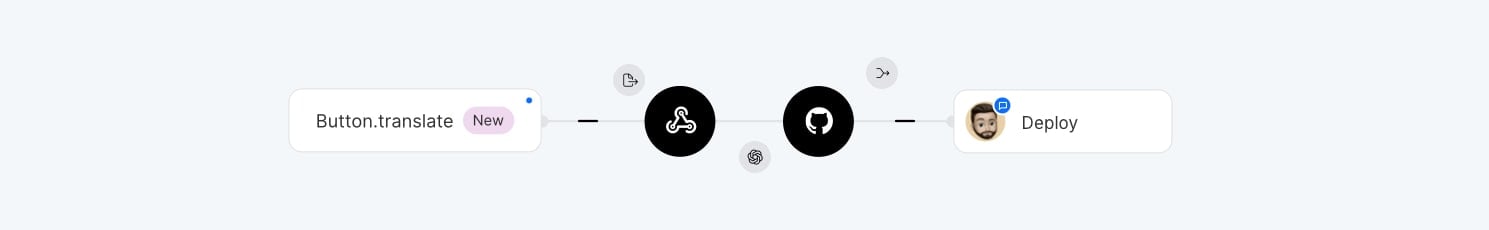
CI/CD after translation changes
This workflow triggers your CI/CD pipeline automatically after translations are updated, enabling automatic deployment of localized builds. The below example uses GitHub Actions, but similar setups can be done with other CI/CD systems.
Steps:
- New strings are pushed to the repository.
- Configure a SimpleLocalize webhook to trigger on
CHANGEevents in the translation editor. - Set up a GitHub Actions workflow to listen for
repository_dispatchevents and run your build/deploy pipeline:
name: SimpleLocalize GitHub Action
on:
repository_dispatch:
types:
- simplelocalize_change
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
// Build and deploy your application
- Your pipeline runs whenever translations are updated in the editor.
Description:
This is a great choice for teams tightly integrating localization with CI/CD and wanting to ensure translations are always included in builds without manual triggers.
The downside is it may cause frequent builds, which can be costly or time-consuming if not managed carefully.
Summary
Here's a summary of the different AI-powered localization workflows and their pros/cons:
| Workflow | Automation level | Pros | Cons | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLI + manual control | Low | Full control, manual review | Slower, more manual steps | Teams wanting control without full automation |
| CLI + GitHub Actions | Medium | Automates extraction and translation; allows review | Still requires manual deployment step | Teams using GitHub, want some automation |
| Fully automated publication | High | Fully automated translation and publishing | Translations may go live without review | Teams prioritizing speed over perfect accuracy |
| i18next continuous localization | High | Always up-to-date translations | May create unused keys, requires cleanup | Apps with frequent string changes |
| CI/CD after translation changes | High | Automatic deployment after translation updates | Frequent builds, may be costly | Teams with tight CI/CD integration |
You can mix and match these approaches based on your team's needs. For example, you might use CLI + manual control for critical strings but automate everything else.
Best practices for AI-powered localization
When using AI for translations, keep these best practices in mind:
- Write clear source strings for better AI output.
- Preserve placeholders (
{username},%s) as some AI models can rewrite or drop them if not instructed properly. - Include context (key descriptions help models translate accurately).
- Review high-impact strings manually before release (marketing copy, UI-critical text).
- Batch API requests to reduce cost and improve speed.
Note that AI should assist human translators, not replace them, especially for critical content. AI gives translators a head start and helps them focus on quality rather than repetitive tasks.
Developer-friendly workflow features in SimpleLocalize
AI translation is just the start. SimpleLocalize offers developer-oriented features that fit into your existing stack:
- MCP Server for secure, controlled translation workflows (Introducing MCP Server)
- Automatic message extraction from source code using AI and i18n-wizard (i18n-wizard guide)
- Translation memory for consistency and cost savings
- Version control friendly JSON/YAML formats
- CLI and API for automation and CI/CD integration
- Webhooks for real-time updates
- Public translation suggestions and AI fixes directly in the editor
By weaving AI into your localization pipeline, from string extraction to deployment, you can keep your product global-ready without slowing development.