AI-Powered Translations. A Comprehensive Guide
Translation services have been around for a long time, but with the growth of artificial intelligence, the field of translation has been revolutionized. AI-powered translations are a fast and efficient way to translate text from one language to another, and they are being used in a wide range of applications, including software localization and content translation.
In this guide, we will explore the world of AI-powered translations, how they work, and how they can be used in software localization.
Table of contents
What is AI translation?
AI translation is a technology-driven approach to translating text from one language to another using artificial intelligence. Unlike traditional translation methods that rely heavily on human translators, AI translation makes use of machine learning algorithms and neural networks to deliver translations that are both rapid and accurate.
How does AI translation work?
AI translation works by using machine learning algorithms to analyze and understand the text that needs to be translated. These algorithms analyze the structure, context, and meaning of the text and then generate a translation that aims to be both accurate and natural-sounding. This process involves several stages, including:
- Text preprocessing: The text is cleaned and prepared for translation, removing any unnecessary characters or formatting.
- Language detection: The algorithm identifies the language of the text that needs to be translated.
- Analysis: The AI system breaks down the text into its grammatical and syntactical components, understanding the context and nuances.
- Translation generation: Based on the analysis, the system generates a translation, often using vast databases of bilingual text corpora to enhance accuracy.
- Post-processing: The translation is refined and polished to ensure that it is accurate and natural-sounding in the target language.

Types of AI translation
AI translation can be broadly categorized into several types based on the underlying technology and approach:
-
Rule-based machine translation (RBMT): a traditional approach that uses predefined rules and linguistic patterns to generate translations. While it can be accurate for simple sentences and specific language pairs, it struggles with complex text or idiomatic expressions.
RBMT was originally used by early translation software like SYSTRAN.
-
Statistical machine translation (SMT): uses statistical models to generate translations based on large bilingual text data. It learns translation patterns from data, improving over time with more data. It can struggle with rare or unseen words, producing unnatural or incoherent translations.
Google Translate and Microsoft Translator used SMT in early versions but have since transitioned to neural machine translation.
-
Example-based machine translation (EBMT): relies on a database of pre-translated sentence pairs and finds the best match for new translations. It is effective for translating phrases or sentences that have been seen before but can struggle with new or unseen text.
-
Neural machine translation (NMT): uses artificial neural networks to create more fluent and contextually appropriate translations. It is capable of understanding the nuances of language better than RBMT and SMT, making it the most advanced and widely used method today.
It is currently used by Google Translate, DeepL, and other leading translation services.
-
Hybrid machine translation: combines the strengths of different methods to improve translation quality. For example, it may use RBMT for grammar and syntax and NMT for context and fluency.
It is used by some translation services, like SDL Trados, to achieve better results than using a single method.
What is generative AI translation
Generative AI translation is a type of AI that uses generative models to make translations. Unlike traditional AI translation models that rely solely on pre-existing text corpora, generative AI models, such as those based on transformers (e.g., GPT-4), can generate text that is not only accurate but also contextually appropriate and creative.
These models are trained on vast amounts of data and can produce translations that are more nuanced and sophisticated, capable of handling idiomatic expressions, cultural references, and complex sentence structures.

Machine translation vs Generative AI translation
Machine translation (MT) and generative AI translation both serve the purpose of translating text using artificial intelligence, but they differ significantly in their methodologies, capabilities, and outputs. Here's a detailed look at the key differences:
- Technological basis: Machine translation relies on statistical models (SMT), rule-based systems (RBMT), or neural networks (NMT) to generate translations. Generative AI translation uses advanced generative models like transformers (e.g., GPT-4) to produce translations.
- Approach to translation: Machine translation focuses on translating text from one language to another, aiming for accuracy and fluency based on pre-existing text corpora. Generative AI translation goes beyond translation to generate text that is contextually appropriate, creative, and nuanced, producing more natural and human-like results.
- Quality and accuracy: Machine translation can produce accurate translations for common phrases and sentences but may struggle with idiomatic expressions, cultural references, or complex text. Generative AI translation can handle these nuances and deliver translations that closely resemble human language proficiency.
- Resource requirements: Machine translation requires large bilingual text corpora for training and may need frequent updates to improve translation quality. Generative AI translation needs vast amounts of data for training but can generate translations that are more contextually appropriate and creative.
- Use cases: Machine translation is suitable for general translation tasks, such as website localization, document translation, or communication. Generative AI translation is ideal for applications where tone, style, and context are crucial, such as literary translation, marketing materials, or customer service interactions.
AI translation in software localization
AI translation is essential for software localization, making it easier and faster to translate software interfaces, documentation, and content into various languages. Traditional machine translation methods, like Neural Machine Translation (NMT) used by Google Translate and DeepL, ensure consistency and speed, allowing large volumes of text to be processed quickly.

Generative AI translation advances software localization by offering context-aware and natural-sounding translations. Unlike traditional MT, generative AI models like OpenAI's GPT-4 handle idiomatic expressions, cultural nuances, and complex sentences more accurately. This results in polished, user-friendly localized content, maintaining the software's tone and brand voice across languages.
Generative AI is especially useful for localizing user-facing elements, such as marketing content and interactive help systems, where engaging and contextually appropriate language is crucial.
How to use AI translation in software localization
The software localization process involves several steps performed by different team members, including developers, translators, and localization managers. To make the most of software localization with AI translation, consider using a translation management system (TMS) like SimpleLocalize that integrates AI translation tools and automates the localization workflow.

SimpleLocalize supports machine translation services like Google Translate and DeepL for fast and accurate translations. Using the dedicated auto-translation feature, you can translate software content in multiple languages with a single click.
It also integrates with generative AI models like OpenAI's GPT-4 for context-aware and creative translations.
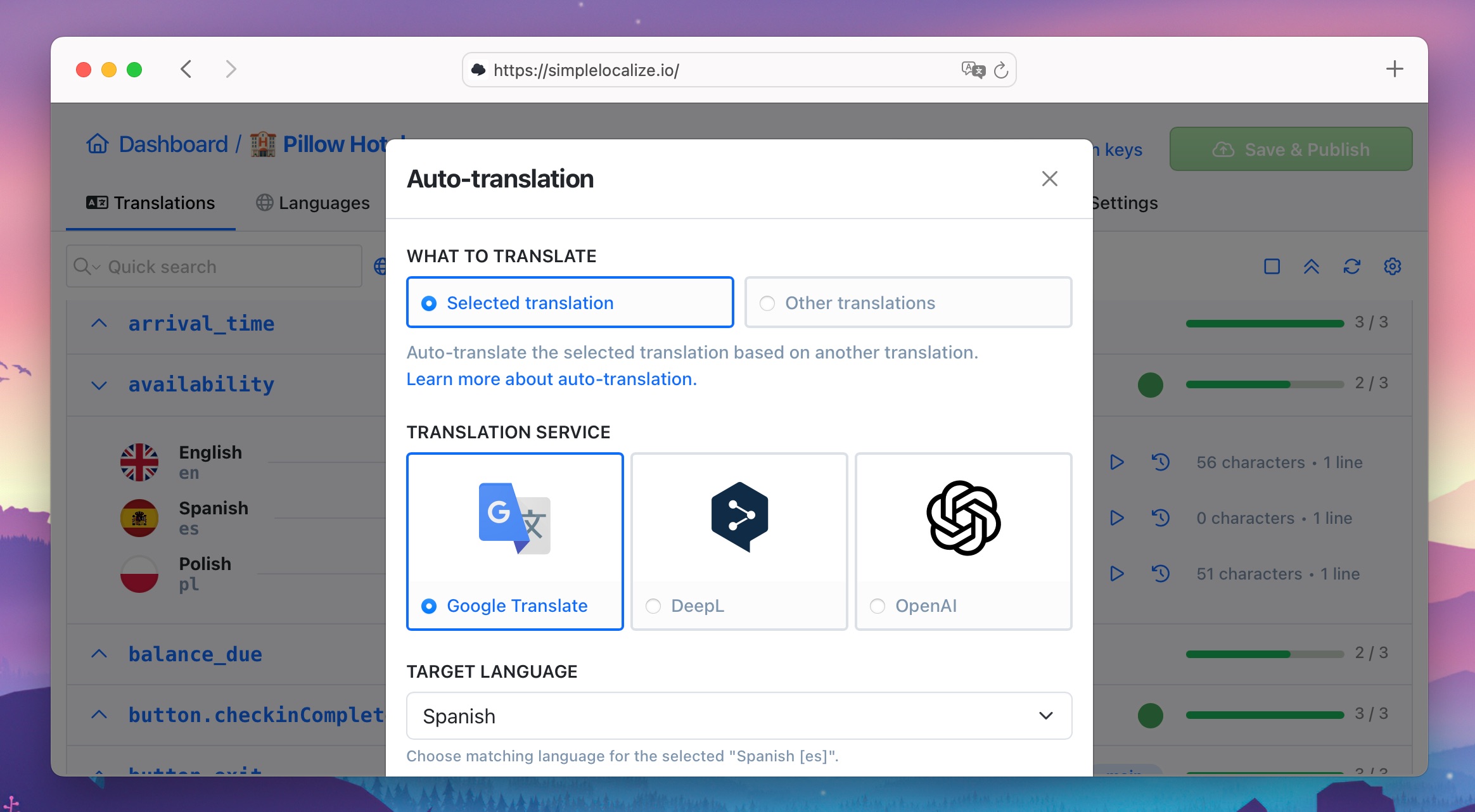
Learn how to get started with translation management using SimpleLocalize
Using AI or gen-AI translations in software localization can significantly improve the efficiency and quality of the localization process, but it's still essential to have human oversight and review to ensure accuracy and cultural appropriateness. SimpleLocalize helps you control the quality of your translations by providing a simple translation editor with a review translations feature.
By using SimpleLocalize, you can streamline the localization process, manage translations efficiently, and deliver high-quality localized content to users worldwide.
How AI translation can help in software localization
AI translation offers several benefits for software localization, making the process more efficient, accurate, and user-friendly by improving:
- Speed: AI translation can process large volumes of text quickly, reducing the time needed for localization projects.
- Consistency: AI translation ensures consistent terminology and style across all localized content, maintaining linguistic accuracy and consistency.
- User experience: AI translation generates natural-sounding translations that enhance the user experience, making the software more accessible and user-friendly.
- Cost-effectiveness: AI translation reduces the need for manual translation, lowering localization costs and improving ROI.
- Scalability: AI translation can handle large localization projects with ease, making it suitable for software with extensive content and frequent updates.
Cons and pros of AI translations
As with any technology, AI translations have their advantages and disadvantages. Here are some of the pros and cons of using AI translations:
Pros
- Speed: AI translations can process large volumes of text quickly, reducing the time needed for translation.
- Cost-effective: AI translations are more affordable than human translations, making them a cost-effective solution for businesses.
- Consistency: Maintains uniformity in terminology and style across different languages.
- Scalability: Easily scales to accommodate multiple languages and frequent updates.
Cons
- Accuracy: AI translations may not always be as accurate as human translations, especially for complex or nuanced text.
- Cultural nuances: AI might miss cultural subtleties, potentially causing misinterpretations or offense.
- Quality: Translation quality can vary depending on the complexity of the content and the language pair.
- Creativity: AI translations may lack the creativity and nuance that human translators
- Over-reliance: Relying solely on AI may overlook the need for human review, especially for high-stakes or sensitive content.
For generative AI translations, the pros, and cons are similar, with the added benefit of more contextually appropriate and creative translations. However, generative AI translations may still struggle with accuracy and cultural nuances, requiring human oversight to ensure quality and appropriateness.
Conclusion
AI-powered translations have revolutionized the language services industry with their ability to provide rapid and efficient translations. By using advanced algorithms and neural networks, these systems handle large volumes of text, delivering translations that are both accurate and contextually relevant.
Generative AI models, in particular, push the boundaries of translation quality by producing more nuanced and creative outputs. However, these models still face challenges with accuracy and cultural sensitivity, requiring careful oversight to ensure high-quality translations.
In software localization, AI tools streamline the process, improve the user experience, and significantly reduce translation costs. Despite their advantages, AI translations should be used alongside human expertise to achieve the best results and address any AI limitations. As AI technology continues to advance, its role in global communication is set to expand, offering even more sophisticated solutions.