Best practices for creating translation keys
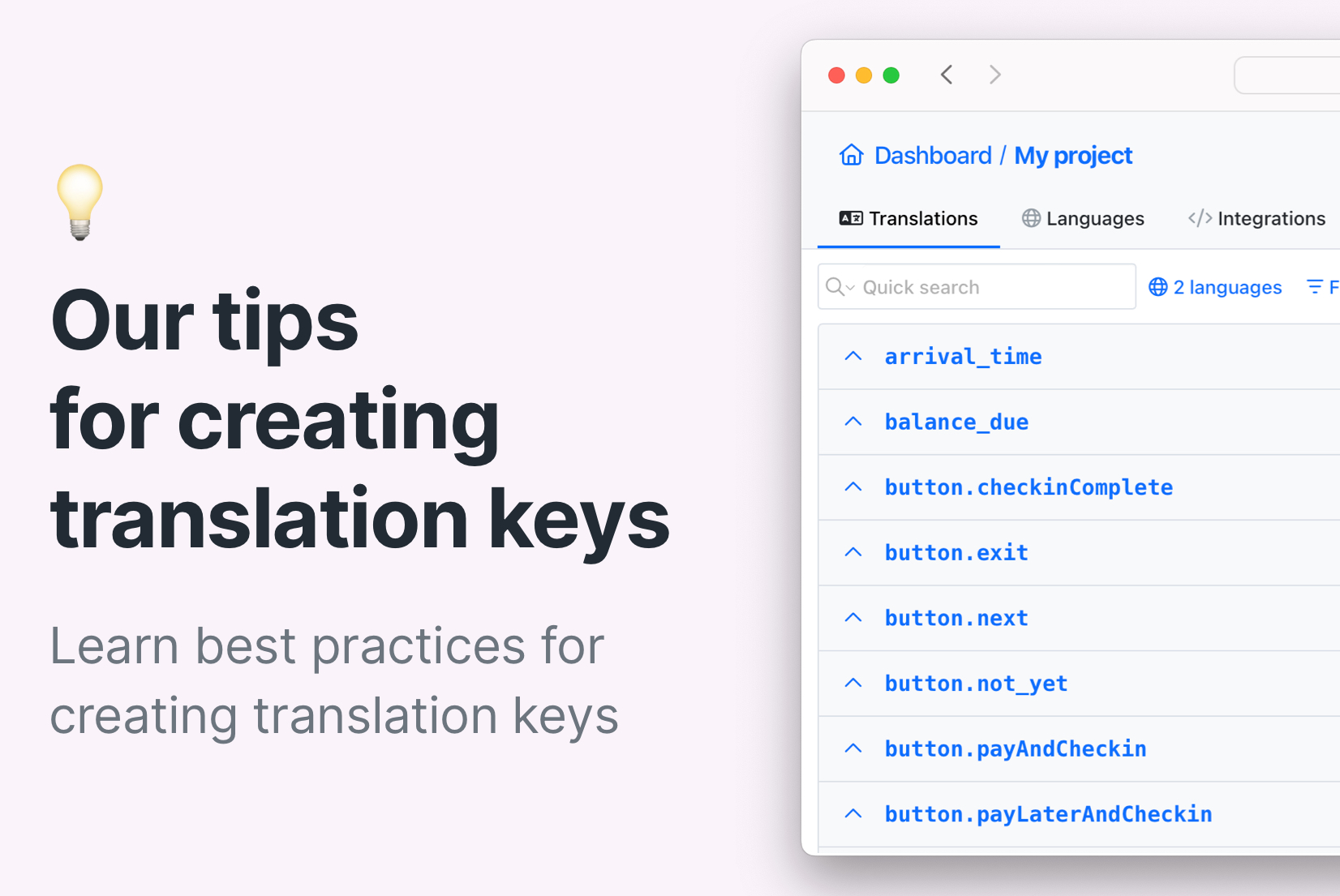
Translation keys are fundamental to software localization, providing a framework for translated content and simplifying the development and localization processes. In this blog post, we'll outline the best practices for creating translation keys, along with tips and tricks to improve your localization workflow. Let's dive in!
Table of contents
Understanding translation keys
A translation key is a reference or identifier used in localization and translation processes, linking the original source text with its corresponding translated content. It works as a guide for translators, helping them accurately match text to its equivalent in another language or dialect.
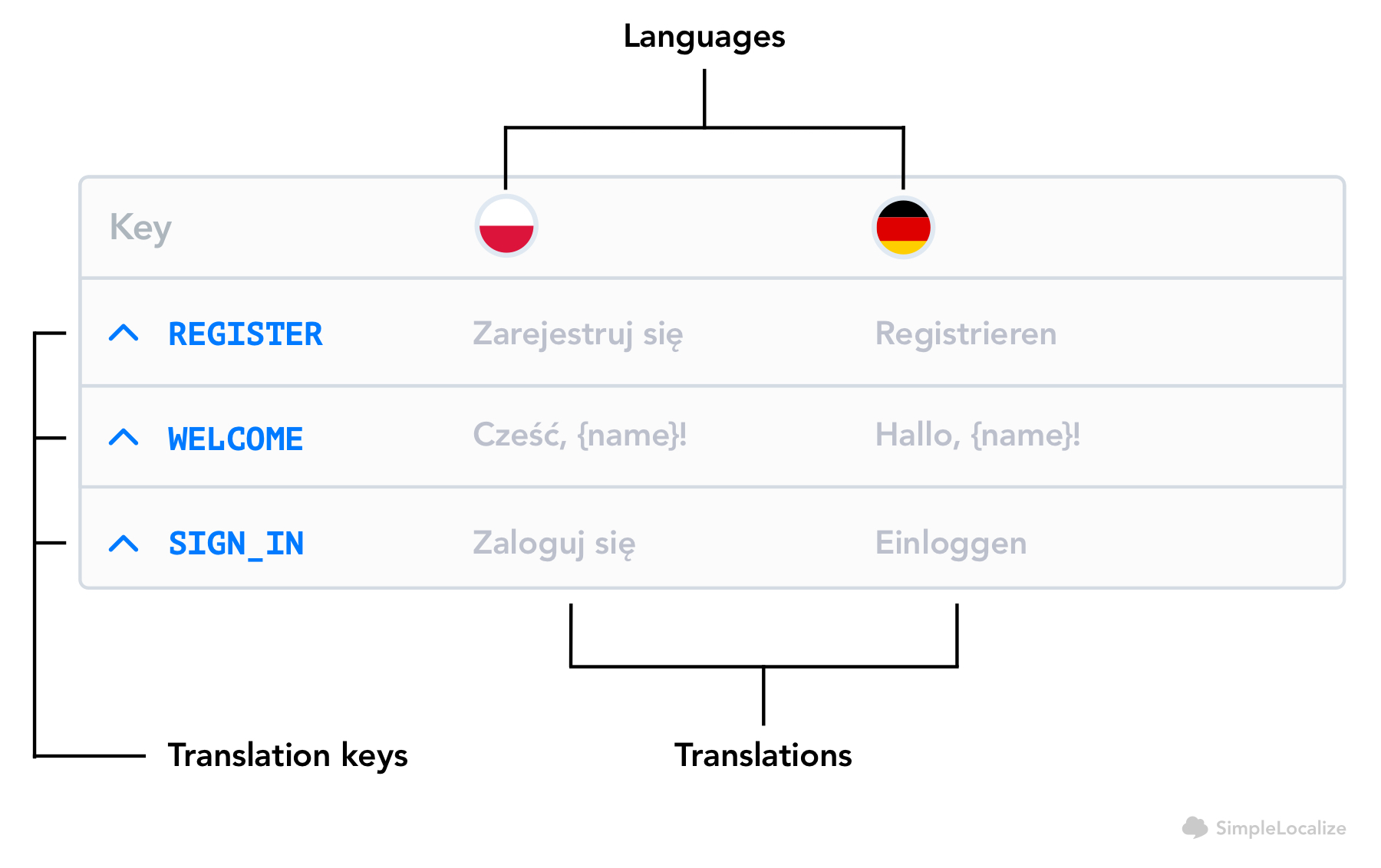
Therefore, the structure and creation of translation keys are crucial for their effectiveness. They should be readable and decipherable while containing sufficient information about the translation context. In the sections below, we will describe best practices for creating translation keys and things to remember when doing so.
To learn more about translation keys and see examples, please refer to our blog post 'What is a Translation Key?' where we explain the concept in detail.
Best practices
Below are some best practices and tips for creating translation keys that are simple, comprehensive, and effective in the software localization process.
Be descriptive
Use descriptive keys that provide a context for the translation. This makes it easier for translators to understand the intended meaning and ensure more accurate translations.
For example, instead of using an abbreviated version like btn_next, opt for a more descriptive version such as button_next.
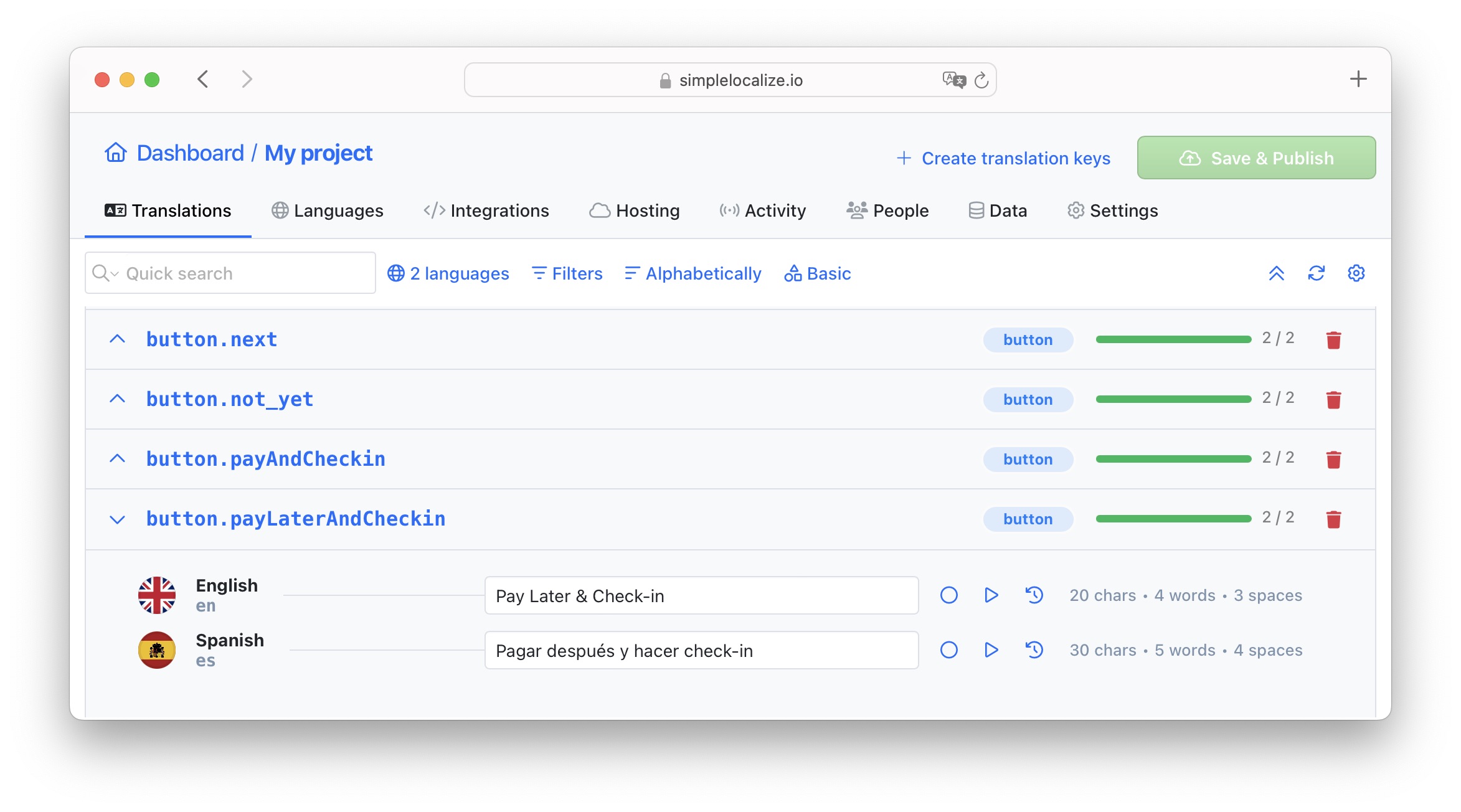
Maintain consistency
Consistency in key naming conventions across the project is crucial to avoid confusion and simplify maintenance.
Choose a format and stick to it; for instance, use log_in and log_out instead of log_in and logOut.
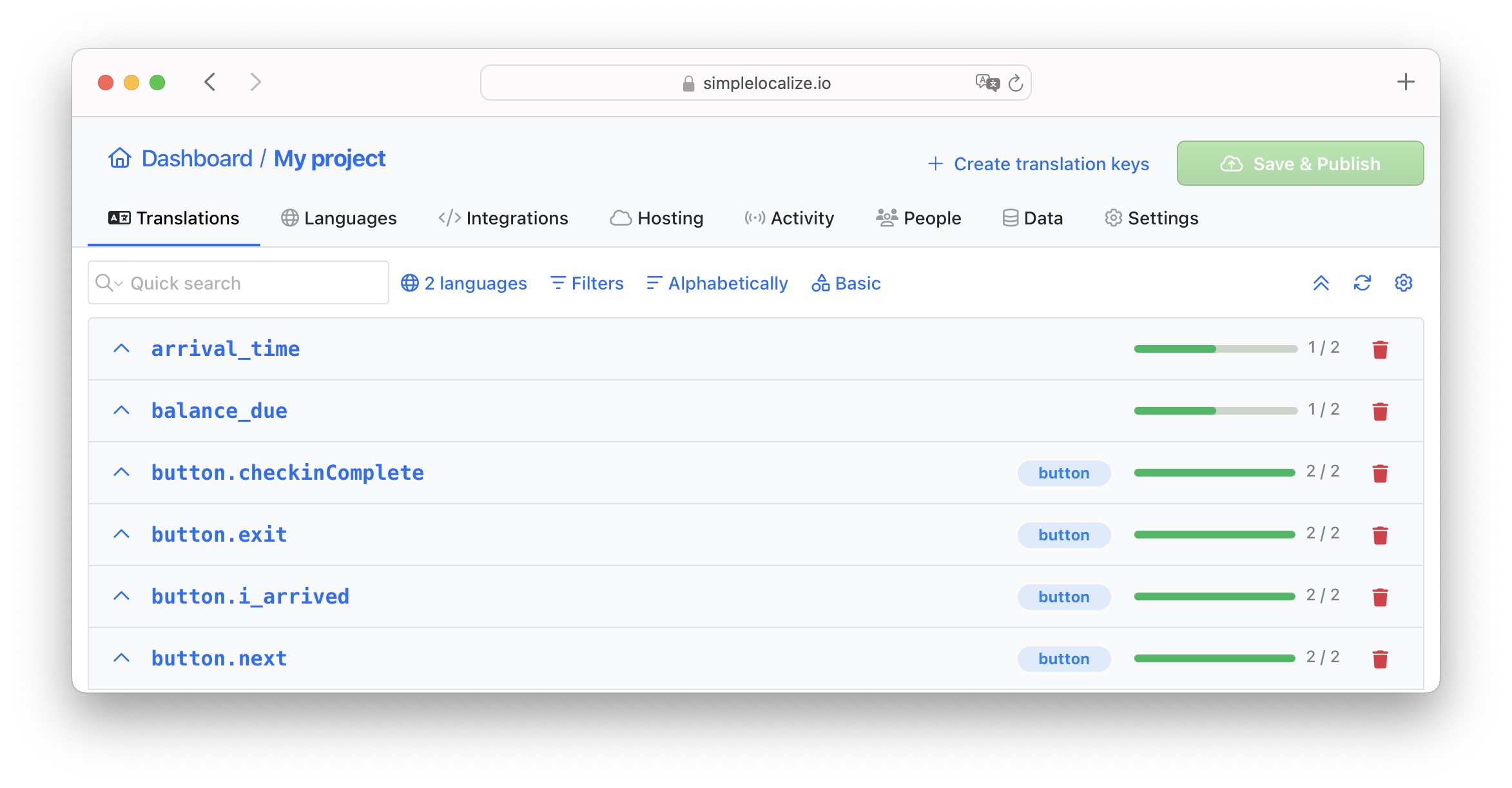
Organize hierarchically
Organize keys hierarchically to reflect the structure of your application. This helps in maintaining a clear and organized translation file.
Include the page or component name before the actual translation key. For example, login.label_username indicates the label text element in the login component, not in any other place in your app.
Avoid over-complicating
Avoid linking keys with placeholders or variables, as this can make translations harder to manage. Instead, include placeholders or variables inside the actual translation.
For instance, use welcome_message translation key with translation Welcome home, {username} instead of translation key including variable: welcome_message_{username}.
Choose meaningful names
Select meaningful names for translation keys that reflect their purpose and usage in the application. Avoid creating unreadable and undecipherable keys like xyz123.
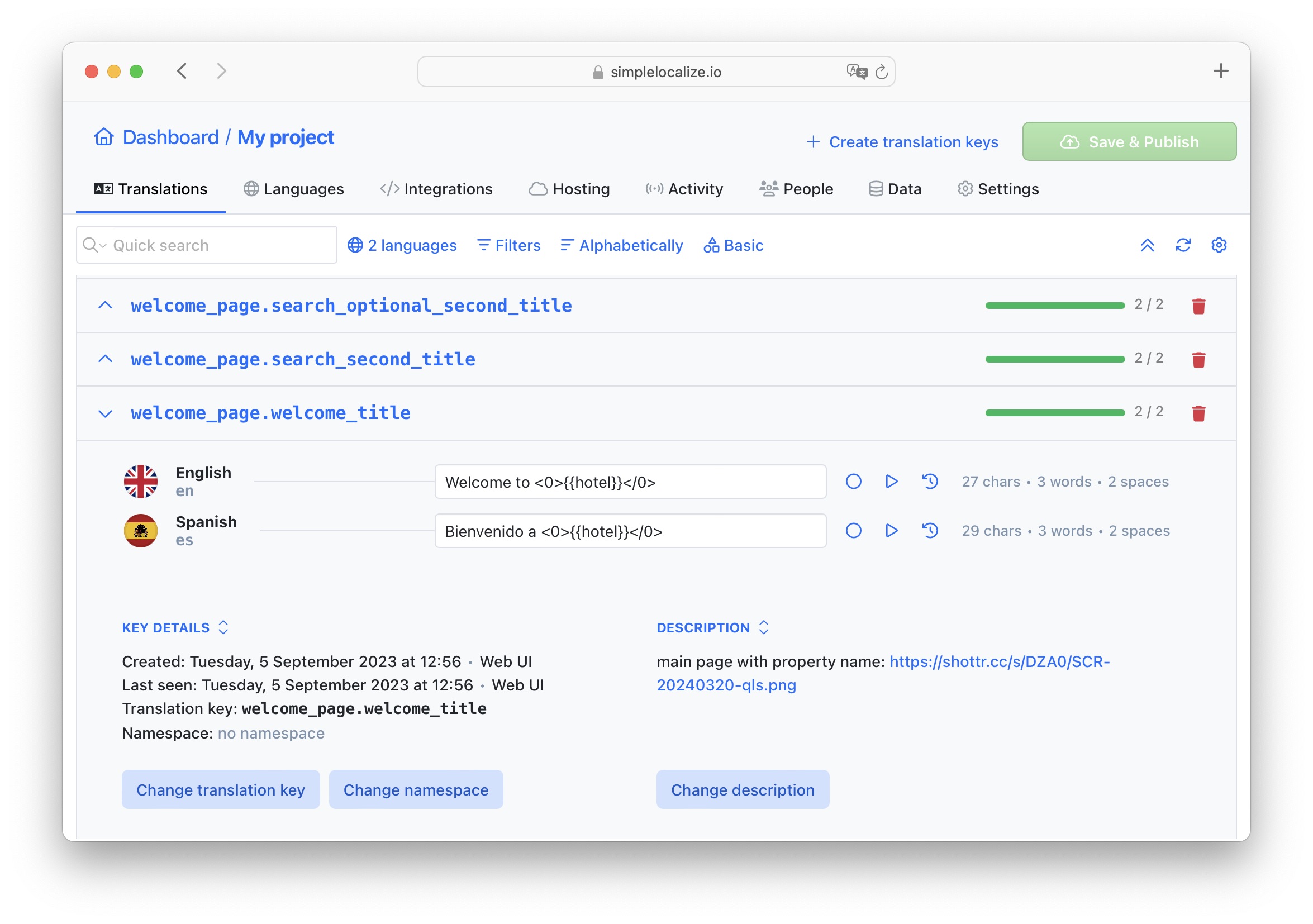
Add key descriptions
Include translation key descriptions directly from the source code to provide translators with additional context or add them directly in the translation editor. This can be done through tools like SimpleLocalize, improving translators' understanding of the translation key's purpose and usage.
Enhance readability
Ensure that translation keys are easy to read for everyone by using dots, camel case, or underscores. Additionally, make sure that translation keys are not too long - they will be harder to read.
Instead of errormessageinvalidemail, create error_message_invalid_email or errorMessageInvalidEmail.
Design for scalability
Design keys to accommodate future additions and modifications to the content. Instead of mirroring the original text 1:1, create unique yet descriptive keys.
For example, instead of welcome.search.enter-your-name-or-booking-id-here, create a simple key welcome.search.label. It will work even if the label text changes over time.
Conclusions
By following the best practices outlined above, you can create translation keys that are clear, consistent, and easy to manage, ultimately improving the localization process. For an optimized localization experience, consider integrating a translation management solution like SimpleLocalize into your workflow.